Functions of The Skeleton











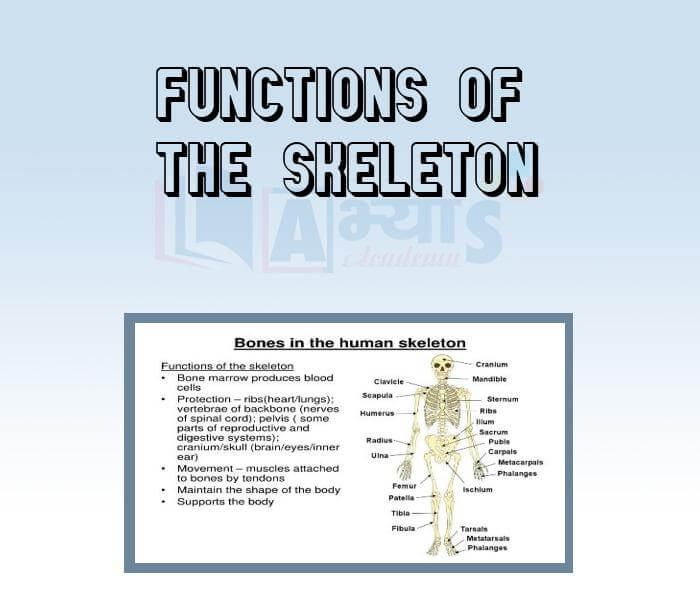
Function of Human Skeleton
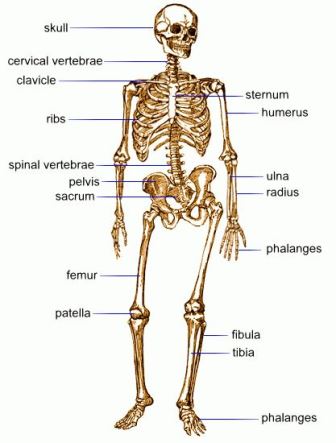
The bones in our body make up a framework called skeleton. The skeleton of an adult human being is made up of 206 bones. A child has many more bones. But as he grows into an adult many of the bones fuse together.
Bones are made of hard substance.Cartilage are soft and elastic. In the bone marrow, red blood cells are produced. Bones are of many shapes and sizes.Some are flat, some are cylindrical and some are spherical.
The longest bone of our body is femur and the smallest bone is found in our ears. Skeleton system extends from the top of our head to the tip of the toes.
Functions of The Skeleton:
The skeleton has four main functions:
I give you shape. Without me, you are like jelly. I give you support like the pillars of a building. I also protect your delicate parts. Who am I? | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Select the function performed by our Skeletal system. | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation |
Man can stand straight because of the ________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
It has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.
